|
Overview Current research interests include applications of statistical learning and computer vision in the arts. |
|
| Projects | |

|
Neural matte extraction without training: The motivation for training a deep learning model is the assumption that it can be trained once and used many times, as in the case of video conferencing with many calls each involving mostly front-facing humans. Visual effects often violates this assumption, as it requires matte extraction from diverse environments and props (underwater, crashed space ship model) many of which will only be seen a few times, and with no easy way to produce training data. This work introduces a training-free approach to neural matte extraction, using the deep image prior to trade computation for data. |
|
Deep Learning without Back-Propagation: This paper (arxiv 2019, AAAI 20) is the first work to demonstrate successful deep net training exclusively using the information bottleneck principle. Training is significantly more expensive than backpropagation, but has potential advantages of avoiding exploding/vanishing gradients and layer-parallel training. Remarkably, the network often spontaneously produces disentangled one-hot output activations. |

|
Universal Image Generator: Hostadter posed the question, "Is there a single algorithm that can generate all possible typefaces". Here we address the generalized question, is there a single algorithm than can generate all possible images? |

|
Direct Manipulation Blendshapes: Direct manipulation for figure animation has long been possible using inverse kinematics. This work describes an easy-to-implement direct manipulation approach for the popular blendshape facial representation. It also interoperates with traditional blendshape parameter (slider) editing, unlike face editing approaches based on an underlying PCA representation. This is crucial, since a simple mathematical argument shows that direct manipulation is sometimes less efficient that parameter editing, while the converse is equally true in other cases. |
|
VisualIDs: User interfaces need scenery, and suitable scenery can be invented with computer graphics techniques. |

|
Pose Space Deformation is a creature skinning/deformation algorithm that combines aspects of skeleton-driven skinning and blendshapes and improves on each. skinning.org chapter on PSD and related techniques and background math, older notes, code examples, video. |

|
1) This sketch introduced the texture-space diffusion approach to subsurface scattering for skin,
developed for the Matrix sequels by George Borshukov and myself
(Siggraph 2003 sketch)
.
The TSD idea was developed and extended by
ATI
(see also)
and Nvidia incorporated the idea as part of their approach to
real-time skin rendering.
TSD is now widely used in real-time subsurface approaches.
2) The UCAP dense markerless face capture used on Matrix sequels. slides (Also see these other Matrix virtual actor sketches: hair, cloth) |

|
Mapping the mental space of game genres. Starting from a large online survey, we use a classical psychological scaling technique, updated with a modern manifold learning approach, to algorithmically produce maps of the mental space of video game genres. |

|
Limits to software estimation. Can the prediction of development schedules and the assessment of programmer productivity and software quality be codified and reduced to formula? No: algorithmic complexity results can be directly interpeted as indicating that software development schedules, productivity, and reliability cannot be objectively and feasibly estimated and so will remain a matter of intuition and experience. Large Limits to Software Estimation Supplementary Material, link to Slashdot discussion |

|
Perceptual segmentation for NPR sketching. Existing NPR sketching schemes have segmented strokes using relatively simple measures such as curvature extrema. These schemes disregard the successive approximation nature of sketching -- that large details are sketched first, and small details (even if they contain curvature maxima) are only added later. This Graphite05 paper shows that spectral clustering can better approximate the perceptually guided successive approximation used in sketching. |

|
Face inpainting. Which of these two people has thicker lips? A web survey shows that humans find this question well posed and are usually able to guess correctly. This suggests that population face statistics can guide face inpainting. On the other hand, we find that face proportion statistics are clearly non-Gaussian, so simple PCA based approaches will leave room for improvement. We extend an active appearance model to employ local, positive-only reconstruction, resulting in surprisingly good extrapolation. |

|
Feature tracking. "Fast Template Matching", Vision Interface 1995. Describes a frequency-domain algorithm for normalized cross-correlation;
it introduced the integral images idea to computer vision and image processing.
This low-level vision algorithm has been used in phone cameras, astronomy, and medical imaging as well as VFX.
This algorithm is included in the Matlab image processing toolbox and
used in several commercial software packages.
conference paper, expanded/corrected version: .pdf, ps.gz, html. |

|
Generalized fractals. "Generalized stochastic subdivision", ACM Transactions on Graphics July 1987 applies estimation theory to remove artifacts in the popular fractal subdivision construction and generalize it to arbitrary non-fractal power spectra (e.g. ocean waves), producing a multiscale texture synthesis. This is an early application of Gaussian Process regression in graphics.
The work is discussed in the book Peitgen and Saupe, The Science of Fractal Images (Springer-Verlag 1988), section 2.6.
The 1987 article with additional figures is here
(pdf,
html preview)
Also see ``Is the Fractal Model Appropriate for Terrain?'', (pdf) |

|
Accelerated Blendshape Animation. Blendshape modelers spend considerable time attempting to make blendshapes that do not interfere. This technique reduces the interference effect in blendshape animation. |

|
Automatic Lip-Sync: Automated lip-synch and speech synthesis for character animation (CHI 87) describes an algorithm for identifying the mouth positions corresponding to speech in an audio soundtrack. Co-articulation was approximated with a now-standard smoothing approach (smoothing splines). The algorithm has been covered in Siggraph character animation courses and is the subject of U.S. Patent No. 4,913,539. |

|
Sparse Convolution is a simple texture synthesis method that can resynthesize some (random phase) textures given a sample. It was introduced in the Siggraph paper (above), and explained in more detail in this siggraph89 paper. This algorithm removes the directional artifacts found in the initial implementation of Perlin noise and has other capabilities. The algorithm has been incorporated in RenderDotC and Houdini. |

|
Coherent Phase Texture Synthesis
(unpublished research) Many texture synthesis approaches produce more or less 'random phase' textures, i.e., coherent sharp 'structural' details are not present. This synthesis algorithm has a coherence knob that can produce such structural details in a synthetic texture. Sample image |
|
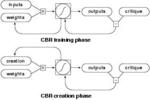
Neural Network pattern synthesis.
"Creation by Refinement" proposed pattern synthesis by classifier-guided neural net denoising of random noise.
Computers at the time were <1Mflop, a factor perhaps 1E9 slower than current GPUs. The work introduced the activation maximization idea later used e.g. in Google's Deep Dream, and also introduced a hard negative mining scheme.
(pdf). |
|
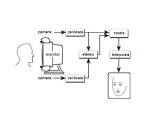
Eye contact by image-based rendering. "Teleconferencing Eye Contact" (joint work with M.Ott and I.Cox at NEC Research). This work addressed the videoconferencing eye contact problem using view morphing (and is one of the earliest publication on these subjects). Two cameras are mounted around the monitor, and stereo reconstruction is used to form a crude 3D depth model which is filled in and smoothed using scattered data interpolation; this model is then used to warp one of the views. A non-real-time implementation of the technique shown at CHI93 demonstrated that within a small range of head orientation, the impression of eye contact is apparently determined by the overall proportions of the facial projection rather than the eye projection specifically, and thus even a low-resolution depth reconstruction provides an impression of eye-contact. This technique is the subject of US patent #5,359,362. |
JP Lewis
Bio & CV
Previous affiliations include Google Research, EA SEED, Weta, USC, Stanford, Interval Research, Industrial Light & Magic, Disney, MIT


